How does diabetes affect the eyes? This question is crucial for millions of individuals living with diabetes, as many may not fully understand the profound impact the disease can have on ocular health. Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body cannot effectively use insulin or produce enough of it, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar can damage various organs, including the eyes, resulting in serious complications and vision loss.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between diabetes and eye health, exploring the various conditions that arise from prolonged high blood sugar levels, preventive measures, and treatment options. By understanding how diabetes affects the eyes, patients can take proactive steps toward maintaining their vision and overall well-being.
The Mechanism Behind Diabetic Eye Diseases

Understanding how diabetes affects the eyes involves examining the underlying mechanisms at work. Elevated blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia, lead to long-term damage to the blood vessels, nerves, and tissues within the eyes. This damage can manifest through several specific conditions, which we will discuss in detail.
The Role of Blood Sugar Levels

Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day and must be carefully managed to prevent complications. Continuous high levels of glucose can cause the blood vessels within the retina to become leaky or blocked.
When these blood vessels are compromised, it leads to poor circulation and inadequate nutrient supply to the retinal cells. This process, called diabetic retinopathy, is one of the most common eye diseases associated with diabetes and can eventually result in blindness if left untreated.
Furthermore, high blood sugar can also affect the lens of the eye, causing swelling and altering its shape; this condition is referred to as diabetic cataracts. Prolonged exposure to elevated glucose levels can accelerate the formation of cataracts, leading to cloudy vision over time.
Insulin Resistance and Eye Health

Insulin resistance is another critical factor contributing to the effects of diabetes on eye health. When the body’s cells no longer respond effectively to insulin, it can lead to various complications, including inflammation in the eye.
Inflammation can adversely affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to conditions like macular edema, where fluid accumulates in the macula, the part of the retina that is responsible for sharp central vision.
The interplay between insulin resistance and eye health illustrates the complex relationship between metabolic disorders and vision. Managing insulin levels through diet, exercise, and medication is essential for minimizing these risks.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams

Regular eye examinations play a pivotal role in catching diabetic-related eye diseases early, especially since many of these conditions can develop without noticeable symptoms initially. Routine checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor any changes in the eyes and intervene before significant damage occurs.
Patients should inform their eye care professional of their diabetes diagnosis so they can perform specialized tests, such as dilated eye exams, to evaluate the condition of the retina and other structures within the eye. Early detection and intervention significantly improve the chances of preserving vision and reducing the risk of blindness.
Common Diabetic Eye Diseases Explained
Several eye diseases are closely associated with diabetes, each presenting unique challenges and treatment options. Understanding these conditions is vital for anyone diagnosed with diabetes.
Diabetic Retinopathy
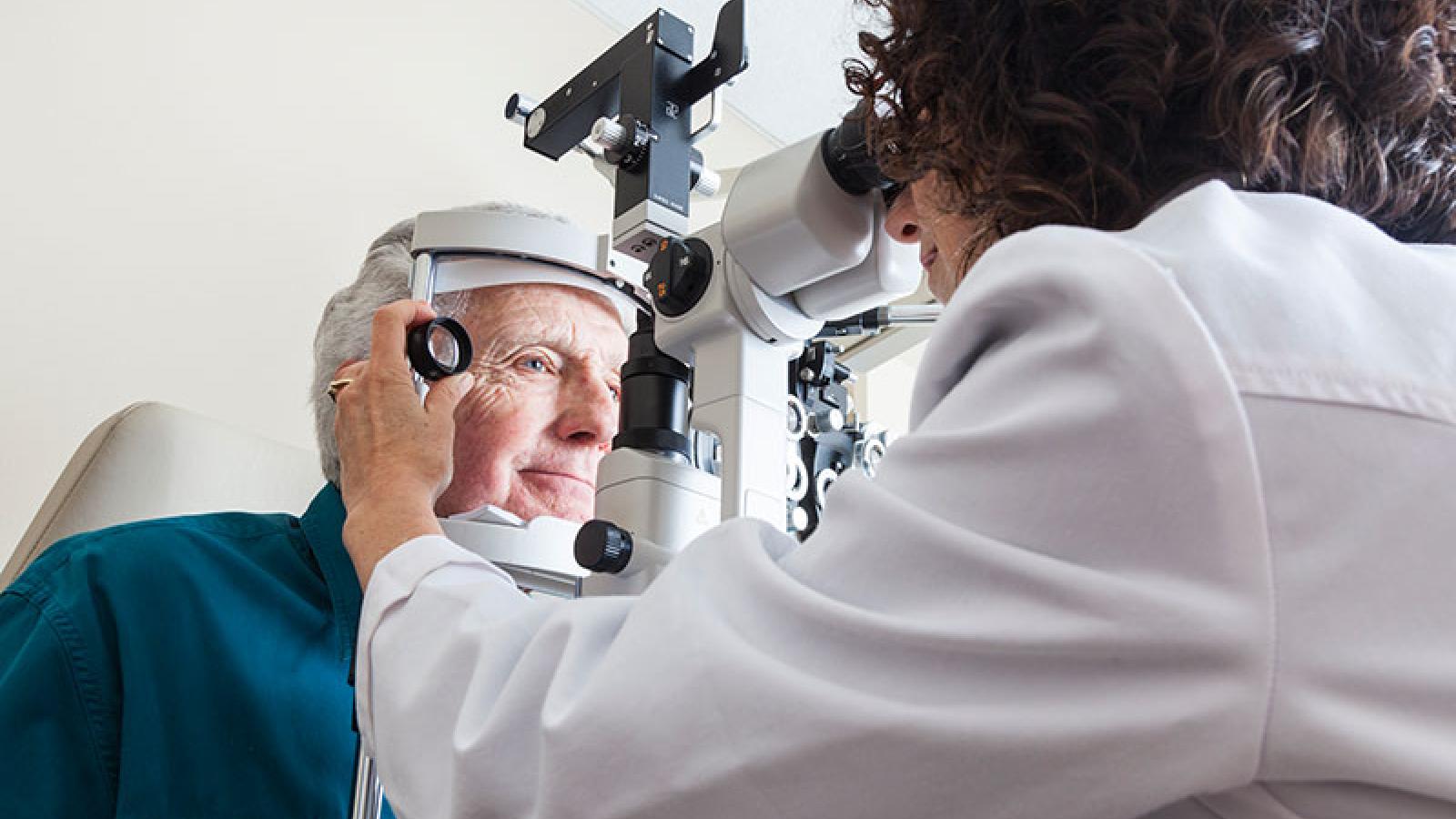

Diabetic retinopathy is perhaps the most recognized complication of diabetes affecting the eyes. As mentioned earlier, this condition occurs due to damage to the retinal blood vessels caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels.
There are two main stages of diabetic retinopathy: non-proliferative and proliferative. In the non-proliferative stage, small blood vessels leak fluid into the retina, which can lead to blurred vision. The proliferative stage is more severe, involving the growth of new, fragile blood vessels that can bleed into the eye and cause significant vision loss.
Managing diabetic retinopathy requires diligent control of blood sugar levels, regular eye screenings, and potential treatments like laser therapy or injections to manage fluid accumulation and stabilize vision.
Cataracts
Diabetic cataracts develop at an accelerated rate in individuals with diabetes compared to the general population. The lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to blurry vision and difficulty seeing at night.
Cataract surgery is a common and effective treatment for this condition, allowing the cloudy lens to be replaced with a clear artificial lens. Post-surgery, patients usually experience a significant improvement in their vision and quality of life.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is another concern for those with diabetes and refers to a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure in the eye. Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing glaucoma, which can lead to blindness if not detected and treated promptly.
Regular eye exams are essential for monitoring intraocular pressure levels, and treatments may include medications or surgical procedures to relieve pressure and protect the optic nerve.
Prevention Strategies for Eye Health

While diabetes poses significant risks to eye health, there are preventive measures that individuals can take to mitigate these risks effectively.
Blood Sugar Control

Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is the cornerstone of preventing diabetic eye diseases. Patients should work closely with their healthcare teams to establish personalized meal plans, exercise routines, and medication regimens that support optimal glucose control.
Lifestyle changes such as adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods, low in processed sugars, and engaging in regular physical activity can greatly impact blood sugar management.
Regular Eye Check-ups
As reiterated throughout this article, regular eye examinations are critical for detecting early signs of diabetic eye diseases. Patients should schedule comprehensive eye exams at least once a year, or more frequently based on their individual risk factors and health status.
During these exams, eye care professionals can identify potential issues and provide guidance on lifestyle modifications and treatments to preserve vision.
Education and Awareness

Knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes and protecting eye health. Patients should educate themselves about the risks associated with diabetes and proactively seek information about diabetic eye diseases.
Engaging with healthcare providers, joining support groups, and participating in educational workshops can empower individuals to take charge of their health and adhere to preventive measures.
FAQs About Diabetes and Eye Health

What are the early signs of diabetic eye disease?
Common early signs of diabetic eye disease may include blurred vision, difficulty focusing, and fluctuations in vision. Some people may notice spots or floaters, and others might experience difficulty seeing at night.
Can diabetic eye problems be reversed?
While some aspects of diabetic eye diseases can be managed or stabilized, reversing existing damage is often challenging. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing further deterioration and preserving vision.
How often should people with diabetes get their eyes checked?
Individuals with diabetes should have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. Those with existing eye conditions or other risk factors may need more frequent visits as recommended by their eye care provider.
Is it possible to prevent diabetic retinopathy?
Preventing diabetic retinopathy largely depends on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and adhering to regular eye exams.
What treatments are available for diabetic eye diseases?
Treatment options vary depending on the condition and severity, but they may include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and cataract surgery. It is crucial for patients to discuss their specific circumstances with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Conclusion

Understanding how does diabetes affect the eyes is essential for anyone diagnosed with this chronic condition. The interrelationship between elevated blood sugar levels and eye health underscores the importance of preventive care, regular screenings, and diligent management of diabetes.
With proper education and proactive measures, individuals living with diabetes can significantly reduce the risks associated with eye diseases and maintain their vision for years to come. Emphasizing blood sugar control, awareness, and routine check-ups will empower patients to take charge of their eye health, ultimately leading to better overall outcomes.
Read Also :


0 thoughts on “Understanding How Does Diabetes Affect the Eyes? – The Unseen Consequences of High Blood Sugar”